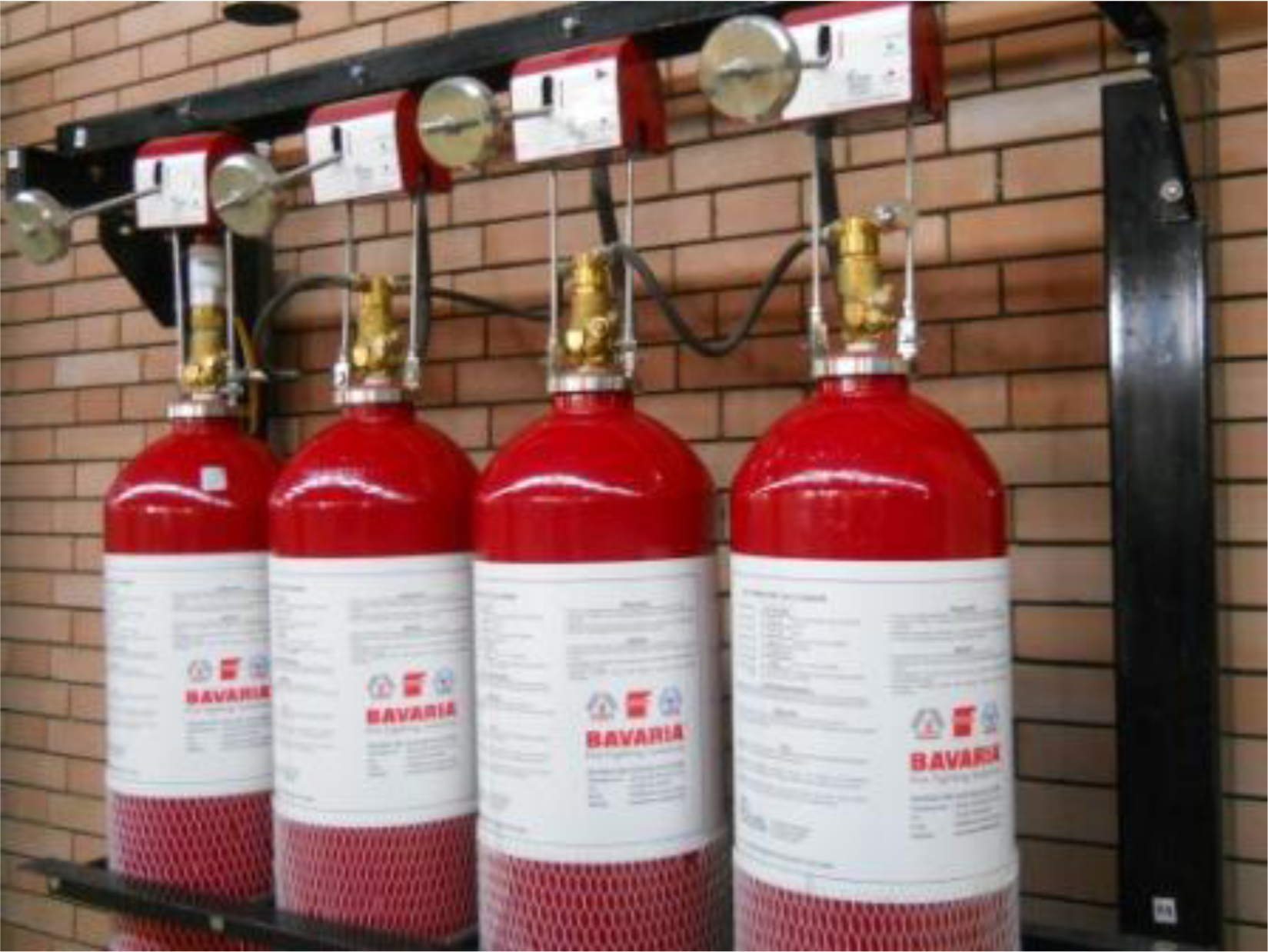
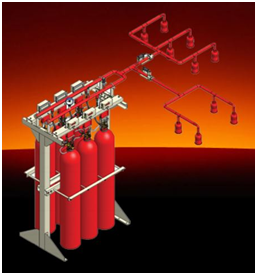
Carbon dioxide systems have been in use since the beginning of the 20th century. The first systems were installed between 1910 and 1915 in Europe. The National Fire Protection Association published its first design standard on carbon dioxide extinguishing systems in 1929. The proper application of carbon dioxide systems is associated with enormous benefits. Attention must be given to personnel safety in order to gain those benefits. The continuous training of personnel does serve this objective also. Carbon dioxide has been used commonly to extinguish flammable and combustible liquids fires, gas fires and fires involving electrically energized equipment. Carbon Dioxide may also be used to extinguish ordinary combustibles. On the contrary, fires involving active metals, metal hydrides and materials that contain available oxygen are not extinguished by carbon dioxide. The use of carbon dioxide is limited by its physiological effects and by restrictions imposed by the hazard itself. As fire extinguishing agent, carbon dioxide is desirable because of the following properties:
-
It is non-combustible
-
It does not react with most substances
-
It is self-propelling
-
It has high ability for penetration and spreading among the hazard area
-
It will not conduct electricity
-
It leaves no residue